Good vision takes a team effort from the eye muscles, eyes, and brain. When the eyes don't work together or one or both eyes have trouble focusing, the brain has trouble understanding what's being seen. This can cause vision problems.
How the eyes work together
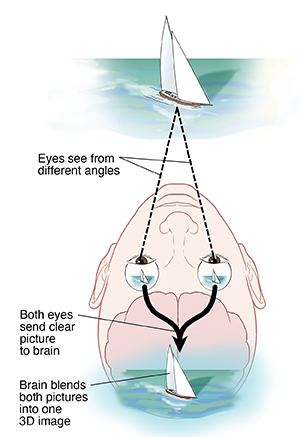
Each eye sees from a slightly different angle. This means that 2 different pictures are sent to the brain. The brain blends these pictures into one 3D image.
When there's a problem
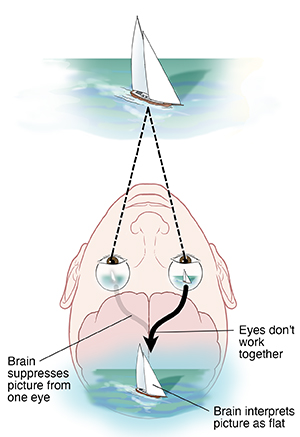
When the eyes don't work together, the brain receives pictures it can't blend together. The brain ignores (suppresses) signals it can't use. In most cases, signals from one eye are ignored. The signals from the other eye are interpreted as a flat image instead of a 3D image. Over time, the brain relies more and more on the other, stronger eye — while vision in the weaker eye gets worse. Because of suppression, normal vision can't develop in the eye that's being ignored. This is called amblyopia.
Symptoms of amblyopia can be hard to notice. Parents may notice signs that their child is struggling to see clearly if they are:
-
Frequently squinting
-
Shutting one eye when trying to get a better look at an object.
-
Tilting or turning their head to get a better look at an object.
-
Having poor depth perception, which may show up as general clumsiness in younger children.
-
Having trouble telling how near or far something is.
Other common eye problems
Alignment problems (strabismus). When one eye turns inward, upward, downward, or outward. This is caused by eye muscles that do not work well together. One eye looks in a different direction from what it's trying to see. This may happen all the time. Or it may happen some of the time.
Focusing problems. One or both eyes have trouble focusing. The brain receives blurry pictures. Focusing problems include:
-
Being nearsighted (distant objects look blurry)
-
Being farsighted (nearby objects look blurry)
-
Having astigmatism (both nearby and distant objects look blurry). In some cases, focusing problems are worse in one eye than in the other.
Other problems. In rare cases, sight in one or both eyes can be blocked. This can be caused by a problem, such as a cloudy lens (cataract). An eye care provider can tell you more about this.