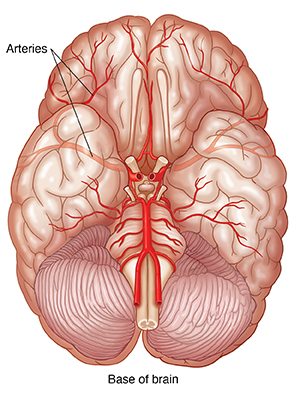
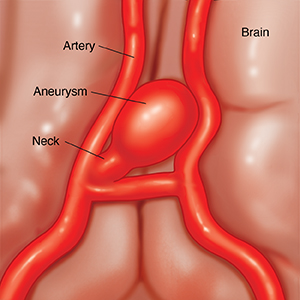
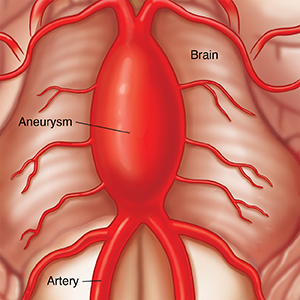
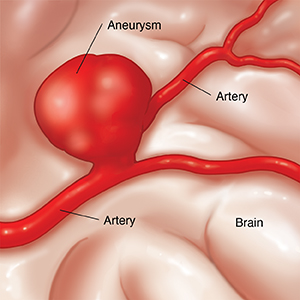
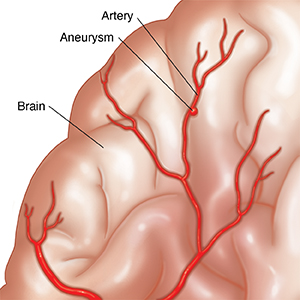
There are several types of brain aneurysms that are classified by shape. These are saccular (also called berry) aneurysms, which are by far the most common. Less common are the fusiform and dissecting types. Brain aneurysms may also be classified by:
-
Size (small, large, and giant)
-
Location
-
Cause (such as a mycotic aneurysm, caused by an infection)
Most aneurysms occur where an artery branches, often at the base of the brain. The risk of an aneurysm bursting (rupturing) can be affected by the shape and location of the aneurysm. The treatment options vary, depending on the type of aneurysm, its size, and its location.
© 2000-2025 The StayWell Company, LLC. All rights reserved. This information is not intended as a substitute for professional medical care. Always follow your healthcare professional's instructions.